
Exports from India agriculture increased by 6.4% to $ 51.9 billion in 2024-25, compared to $ 48.8 billion in the previous year enclosed March 2024. It was against almost stable growth of 0.1% of the value of its global goods exports, against 437.1 billion dollars in 2023-24 to 437.4 billions of dollars in 2024-25.
But the difference was even more in the value of imports. While total imports of goods increased by 6.2% in 2024-24 out of 2023-24 (from 678.2 billion to $ 720.2 billion), agricultural imports increased by 17.2% (from 32.9 billion to 38.5 billion dollars).
A longer period trend (see chart) reveals that India’s agricultural exports decrease between 2013-2014 and 2019-2020, before recovering and culminating at $ 53.1 billion in 2022-2010. Overall, the increase increased from $ 43.3 billion in 2013-2014 to $ 51.9 billion in 2024-25 or just over 20%.
The imports, on the other hand, displayed a more stable expansion of $ 15.5 billion in 2013-2014 at a historic summit of $ 38.5 billion in 2024-25, working at 148%. The surplus of agricultural trade in India has also reduced more than $ 27.7 billion to $ 13.4 billion during this period.
All this comes as India negotiates Commercial agreements With the United States and the European Union, both of which are looking for prices reductions and greater access to the market for their agricultural products.

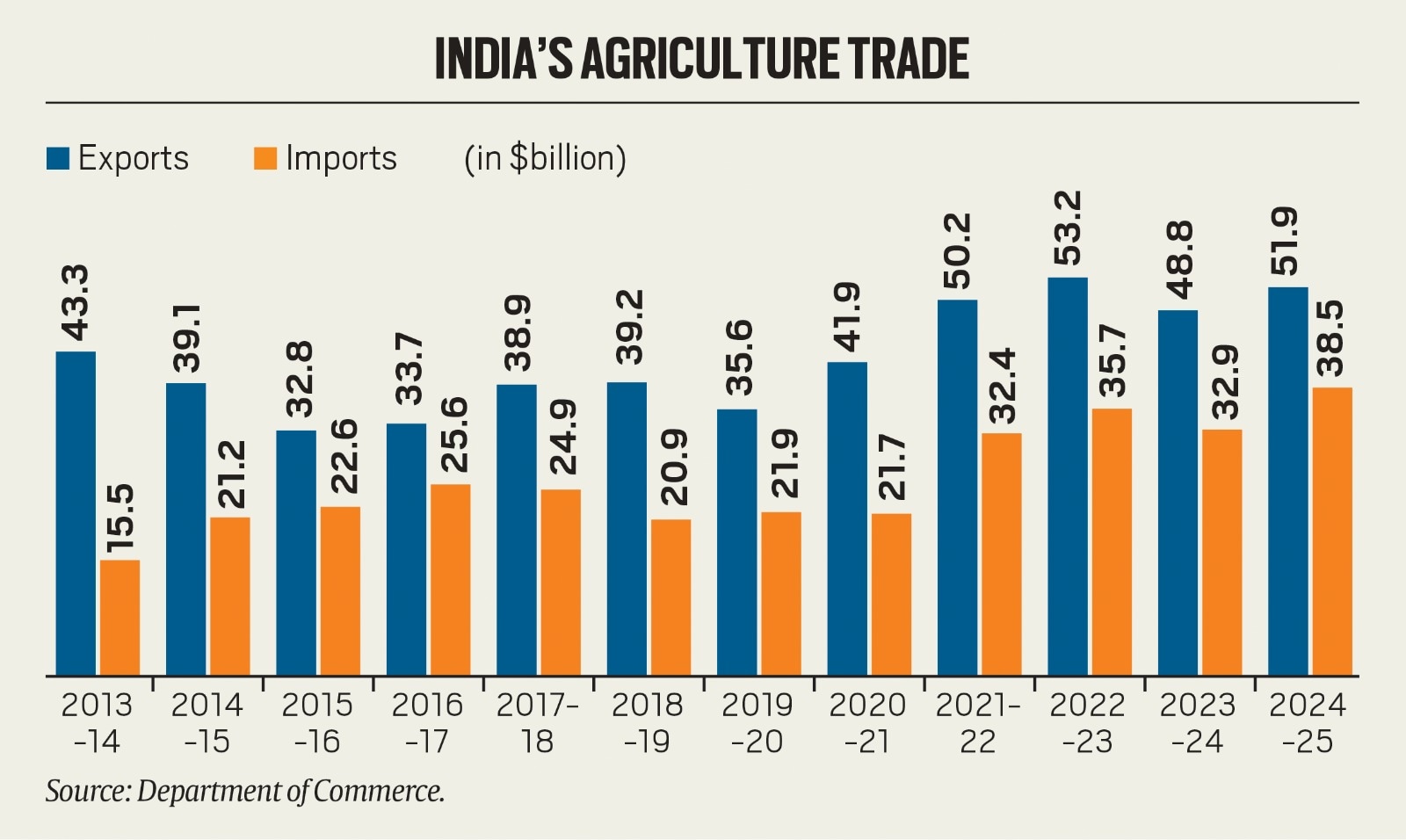 Agricultural trade in India
Agricultural trade in India
Export drivers
Support tables Display the best agricultural export and import items in India, with an annual value exceeding $ 1 billion in one of the last four years.
The story continues below this announcement
Export product No. 1, Marine Products, recorded a drop compared to the top of $ 8.1 billion in 2022-23 to 7.4 billion dollars in the following two fiscals.
India’s marine exports are largely to the United States (around 35%), China (20%) and the EU (15%). Expeditions in the United States, mainly frozen shrimp, now attract 17.7%. This includes the 10% reference rate that US President Donald Trump imposed from April 5. If the latter went up to 26% – Trump suspended this plan until July 9 – it could affect Indian exports.
There are no such concerns with rice, where the value of non-Basmati and Basmati expeditions reached record levels in 2024-25. The 14.1 million tonnes (MT) of Non-Basmati and 6.1 Mt of Basmati rice exports were worth $ 12.5 billion. Most of the Basmati in India goes to Western Asia, while it is Africa for non -basmati grains.
Rice apart, spice exports, tobacco, coffee and fruits and vegetables (fresh and processed) have set new peaks on the last exercise.
The story continues below this announcement
India coffee exports have obtained a boost from the world’s end actions for 2024-25, exhausting at a 25-year-old hollow, at drought in Brazil and the dry time followed by a typhoon in Vietnam. India mainly exports robust beans and powder used in instant mixtures of coffee and espresso. Bad cultures in Brazil and Zimbabwe last year also benefited the Indian tobacco exporters.
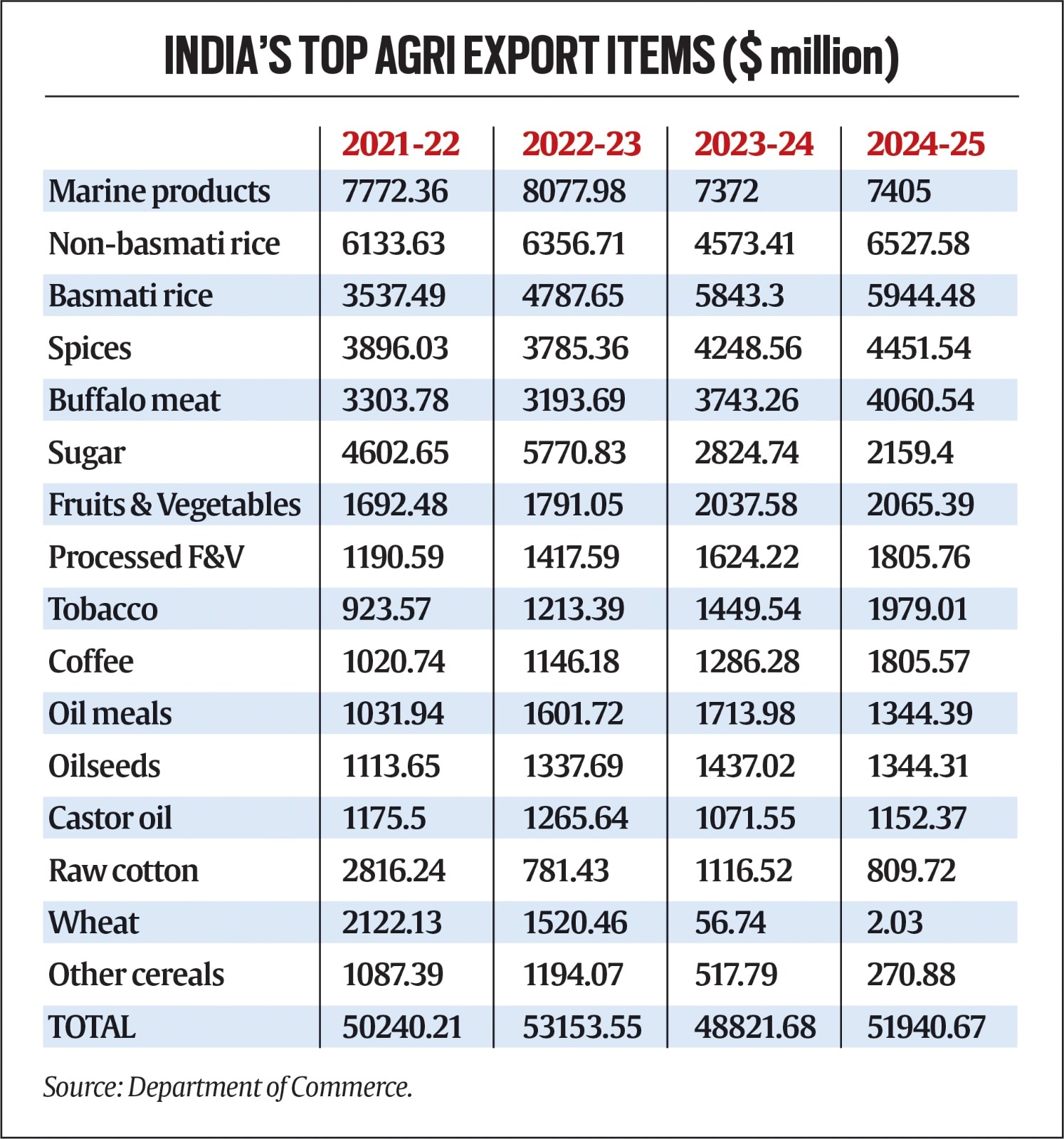 The best agriar exports in India
The best agriar exports in India
Spices are an interesting case, where exports and imports to India have reached record levels in 2024-25. India is a pre -eminent exporter of chili, cumin, mint products, oleorens, curry / paste powder and other non -traditional spices such as turmeric, coriander, fennel, ginger and garlic. On the other hand, it has become a net importer of the two traditional planting spices, namely pepper and cardamom.
The products whose exports have suffered due to the deficits of the domestic offer include wheat, sugar and cotton. The exports of the first two culminated at $ 2.1 billion and $ 5.8 billion in 2021-22 and 2022-2023, but were subsequently prohibited or limited. India continues to export refined / white sugar. However, this comes from the treatment of imported raw sugar, the value of which has increased accordingly.
Cotton is a sad storyWhere exports from India had succeeded $ 4.3 billion in 2011-2012 and $ 3.7 billion in 2012-13. Exports have not only collapsed, but the country has become a net importer of natural fiber. Buffalo meat exports exceeded $ 4 billion in 2024-25, but are still less than $ 4.4 billion and $ 4.8 billion in affected levels in 2013-2014 and 2014-2015, respectively.
Import pilots
The story continues below this announcement
With regard to imports, large tickets remain vegetable oils and legumes.
The low yields by acres compared to rice and wheat, no more equivalent system of public supports of minimum support based on the price, made less viable for Indian farmers to develop the production of oil seeds and legumes.
The result is an arrow import bill. In vegetable oils, it is only partially offset by exports of oil seeds (mainly peanuts and sesame) and residual cake / meal after extraction of oil. Impact imports were evaluated at $ 5.5 billion in 2024-25, exceeding the $ 5 billion mark for the first time.
But it’s not just edible oil and legumes.
Stagnant, if not lowering, interior production also leads to an increase in imports of cotton and natural rubber. Without performance technologies after genetically modified BT hybrids (GM), India cotton production went from 398 Lakh to 291 Lakh balls between 2013-14 and 2024-25. The rubber production has also been on average 8.5 lakh tonnes (LT) in the past three years, from 9 to 9.1 LT to around 2012-23. This, even if internal consumption has increased from 10 LT to 15 LT in the last decade.
The story continues below this announcement
 The best agridans import elements of India
The best agridans import elements of India
The other important elements of agro-import importation are fruits (almonds, pistachios, nuts, apples, dates, figs and raisins, among others), spices (fundamentally pepper and cardamom) and alcoholic drinks.
With the signing of commercial pacts with the United States, the EU and the United Kingdom, we can expect more imports of dried fruit, wines and spirits. In addition, the Trump administration is expected to put pressure on import duties and the softening of non -tariff barriers (in particular with regard to GM crops) on corn, soy and cotton.
All this will finally reflect in agricultural exports of India, imports and excess – if it is narrowed even more.





